[cmamad id=”13606″ align=”center” tabid=”display-desktop” mobid=”display-desktop” stg=””]
It may not be genetic. Chances are that allergies from certain foods make hair fall out. Here’s what you need to be aware of…
—–Important Message——
What gets a girl interested in doing it again and again?
No, it’s not novelty.
It’s not new positions.
It’s not bigger orgasms and it’s not toys.
The secret to building her desire is to build your OWN sensation.
Weirdly, the more YOU feel, the more SHE feels.
Isn’t that the strangest thing ever? Yet it is true, ALL the time.

Don doesn’t mince words, so you get the picture.
I have discovered these methods that build more sensation in YOU make her more interested in doing it…
—————-
Can hair loss be an allergic reaction to this food?
There is good reason to think that food allergies could contribute to hair loss, as well as to general inflammation.
Allergies have been shown to cause some forms of alopecia (hair loss).
And certain immune markers have been found in relation to male-pattern baldness.
There is very good evidence for this.
And this ties in perfectly with some other findings.
The immunosuppressive drugs Cyclosporine and FK‐506 are probably the most effective treatments for causing new hair growth.
This is because they inhibit the very production of interferon-γ (interferon-gamma).
[cmamad id=”13607″ align=”center” tabid=”display-desktop” mobid=”display-desktop” stg=””]
Interferon-γ) is a cytokine – a small protein basically produced only in T cells.
This cytokine travels through the blood and lymphatic system, and into other cells.
Once inside the cell, it upregulates the transcription of phospholipase A₂ (an enzyme that powerfully contributes to prostaglandin formation).
Interferon‐γ is undoubtedly a killer particle.
Mice bred to express interferon‐γ have alopecia, and mice bred without interferon‐γ receptors are resistant to alopecia.
“Interferon-γ is induced by a unique set of stimuli and is produced only by T lymphocytes and natural killer cells.”
Like cortisol and prostaglandin D₂, interferon‐γ is basically synonymous with hair loss.
Food reactions can induce and release this cytokine.
Some of the most direct proof that cytokines such as interferon‐γ cause hair loss comes from Valerie Randall:

This was a strange but powerful demonstration.
The scientists took cells from both balding areas and non-balding areas.
They multiplied those cells in dishes.
And then they collected the fluid the cells were bathed in.
They added this fluid to hair follicles they got from mice.
Then they recorded how much the hair grew over the course of days.
Check out this study…
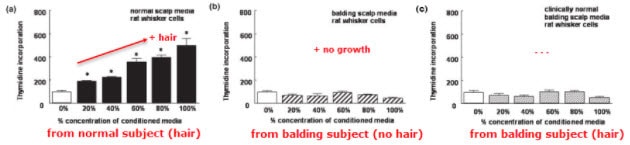
The soluble cytokines and growth factors released from normal cells undoubtedly induced and/or allowed hair growth…
But the cytokines and growth factors released from balding cells completely inhibited it.
Even cytokines from the haired areas of balding subjects (the people, not the mice) inhibited growth (see the rightmost↗ graph).
“These inhibitory factors probably cause the formation of smaller hairs in male pattern baldness.”
Obvious inhibitory factors were secreted because, even in just plain water, test follicles will grow.
Essentially, it must be a cytokine, a peptide signaller.
Steroid hormones (other than cortisol maybe) aren’t very soluble in water.
And neither are prostaglandins.
So which cytokine is doing this?
What causes it, and how can men make it stop?
Luckily, there have been enough studies done to help us fully understand this… and to narrow down the primary agents.

Most cytokines have actually been tested individually on hair follicles.
The hair follicle contains many cell types – it can respond to cytokines and growth factors of all types.
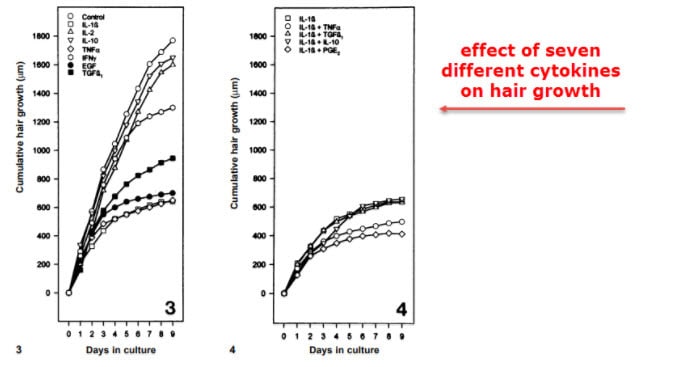
Some cytokines don’t do much in relation to hair growth, so you don’t have to worry about most of them.
And one of them, interleukin‐10, has actually been found by some studies to be protective.
It stimulates growth by inhibiting other cytokines.
Some of the more powerful ones, like tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNFα), are encountered less often.
Much has been written about transforming growth factor beta (TGF-β) – it’s a cytokine that’s upregulated by cortisol.
It increases cyclooxygenase activity within the cell.
This enzyme helps to create inflammatory and hair‐killing prostaglandins.
And interferon‐γ does the same thing but in a different way.
This cytokine is more specialized. And it’s only created in certain cell types in the immune system – the T cells.
Interferon‐γ upregulates the enzyme that’s actually responsible for initiating the prostaglandin cascade. That enzyme is phospholipase A₂.
Phospholipase A₂ splits arachidonic acid from the cell membrane (the only precursor for prostaglandins).
Even days after this happens, the cell can still be releasing arachidonic acid and creating prostaglandins.
Prostaglandin D₂ was the primary factor Luis Garza found to be associated with hair loss.
It seems that all paths ultimately converge at prostaglandins.
Interferon‐γ reactions are one of those paths.
Small changes in rat or mouse DNA can cause hair loss.
I’m sure you were wondering about that.
Changes involving the cortisol pathway and the prostaglandin pathway have previously been shown to do this.
And expressing interferon‐γ in the skin has also done this.

In this study, they spliced the DNA into a keratin gene. This way, it’s produced in the skin only.
This led to hair loss in the mice (see balding mice in the picture below):
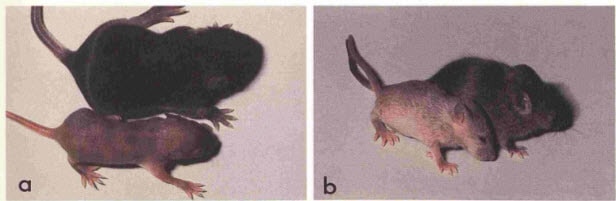
“…a type of hair loss that looks remarkably similar to the type resulting from excessive phospholipase A₂.”
This looks remarkably similar to what happens to mice that are overexpressing COX-2, the other main enzyme.
Phospholipase A₂ and COX-2 work in tandem to create prostaglandins.
“Interestingly, elevated interferon‐γ expression has been reported in the human condition alopecia areata.”
So it should be no surprise that drugs that totally prevent interferon‐γ cause hair growth.
Actually, this is the most commonly reported side-effect of Cyclosporine.
When hair growth occurs via Cyclosporine treatment, the greatest change in cytokines is found with interferon‐γ. How about that?
And there’s lots more evidence that interferon‐γ causes hair loss.
But we need to know how to prevent this.
This cytokine can be induced by tropical diseases and infections.
But it’s more likely to happen to us through foods.
All foreign proteins have the potential to cause an immune response, but some proteins are more allergenic to us than others.
And here’s more about that…

Grains have always been highly associated with food allergies. Especially wheat… and gluten.
Allergies to milk, peanuts, and eggs are very common.
“There can be little doubt that interferon-γ is…the primary cytokine responsible for inducing nonspecific cell-mediated mechanisms of host defense.”
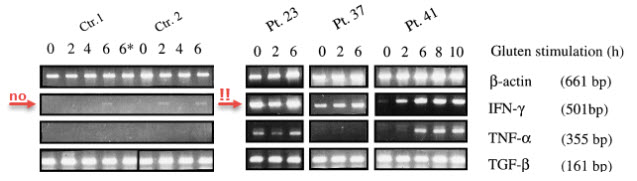
Doctor Nilson’s team took cells from people and grew them for a few days.
Then they added a small amount of gluten to the dish.
They measured the interferon‐γ mRNA (messenger RNA) produced in the cells as a response to the gluten.
In some people, a strong induction of interferon‐γ was seen.
In others, no effect was seen…
Keep in mind that interferon‐γ travels to any cell which has a receptor for it.
It enters that cell and then induces phospholipase A₂ transcription.
This guarantees increased prostaglandin formation – for days or even weeks.
This has been proven very powerfully…
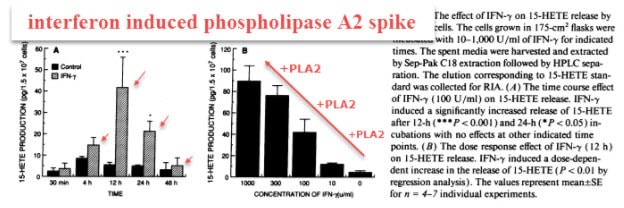
And it seems that this is the main function of interferon‐γ.
All of these cytokines do have their own specific functions…
Some induce COX‐2 production, some induce production of PLA₂ (lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2 – an enzyme). And some just activate PLA₂.
“Stimulation of calcium-sensitive cytosolic phospholipase A2 (cPLA2) synthesis occurs over hours and results in the prolonged release of arachidonic acid and eicosanoid production.”
But in all cases, these cytokines increase prostaglandins.
Cytokines are the link between distal and proximal effectors of inflammation.
Interferon‐γ sits between the adaptive immune system and the primordial, innate immune system.
Prostaglandins do have a good role…
Prostaglandins were the original defense molecule.
They can even be found in plants and single-celled organisms that are under attack.
But this is what you need to know…
Inhibiting prostaglandins means inhibiting inflammation and hair loss.
This comes down to avoiding linoleic acid, inhibiting COX‐2, and avoiding allergenic foods.
Cortisol has its own cytokine, interleukin-1β, with effects that are very similar to those of interferon‐γ.
For this reason (and many others) we need to avoid stress.
“cPLA2 plays a central role in providing arachidonic acid and lysophospholipid for subsequent metabolism to prostaglandins, leukotrienes, [and other] potent lipid mediators of inflammation…
“…the interferon-γ-induced synthesis and activation of cPLA2 may play an important role in mediating the variety of biological functions attributed to this cytokine.”
—–Important Message—–
Have you thought about going gluten-free?
Here is one of many emails I received from the discussion the other day about going gluten-free:

I agree that gluten is part of the problem. I avoid ALL gluten and I’ve never felt better.
Gluten consumption is PART of the problem.
But the gluten-free food fad is not the answer.
What I have found with my students and with me is that increasing good quality FATS and making some minor lifestyle changes can make a world of difference.

——-

http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/j.1365-2133.2006.07144.x/full
Hoffmann, Rolf. "Cytokines and growth factors influence hair growth in vitro. Possible implications for the pathogenesis and treatment of alopecia areata." Dermatological Research (1996)
http://link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1007/BF02505825.pdf
Carroll, Joseph M., et al. "Transgenic mice expressing IFN-γ in the epidermis have eczema, hair hypopigmentation, and hair loss." Journal of investigative dermatology (1997)
http://www.jidonline.org/article/S0022-202X(15)42848-9/pdf
Nilsen, Ellen M. "Gluten induces an intestinal cytokine response strongly dominated by interferon gamma in patients with celiac disease." Gastroenterology (1998)
http://www.gastrojournal.org/article/S0016-5085(98)70134-9/pdf
Wu, Tong, et al. "Interferon-gamma induces the synthesis and activation of cytosolic phospholipase A2." The Journal of clinical investigation (1994)
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC293880/pdf/jcinvest00031-0123.pdf
Farrar, Michael A., and Robert D. Schreiber. "The molecular cell biology of interferon- gamma and its receptor." Annual review of immunology (1993)
https://www.immunology.umn.edu/sites/immunology.umn.edu/files/farrar_wall_of_scholar ship_paper.pdf
https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/hair-loss/symptoms-causes/syc-20372926
https://www.webmd.com/skin-problems-and-treatments/hair-loss/understanding-hair-loss-basics#1
https://www.webmd.com/skin-problems-and-treatments/hair-loss/men-hair-loss-17/hair-transplants
https://bhrcenter.com/laser-hair-regrowth-possible-hair-transplant-work/
Hair loss can be considered as one very stressful part of life, especially for men in today’s modern world. Severe hair loss can cause loss of confidence and can be a source of worry.Hereditary loss of hair can cause baldness in men. Though most people shed close to 50 – 100 hair strands a day which is a natural process, sometimes this intensity can increase. Sometimes men can have circular or patchy kind of bald spots where the skin becomes itchy before fallout. The most common cause of hair loss among men is due to a hereditary condition called male pattern baldness. This type of hair loss can involve hair thinning or miniaturization where the hair becomes soft, short and very fine. The other cause for hair loss is because of hormone imbalance .Problems with the thyroid gland functioning can cause hair loss. There could be scalp infections for example; a ringworm infection can cause scaly patches and hair loss among men.The most challenging of the type of non scarring hair loss is alopecia areata where the body’s immune system starts attacking the hair follicles causing sudden hair loss. Hair loss can also be caused by certain drugs or medications that are used for cancer, heart problems, high blood pressure and birth control. Sometimes the intake of too much Vitamin A can also cause hair loss. Other causes of hair loss may include trigger events that cause high intensity physical or emotional shock. This may include a emotional loss, surgery or any other event that can cause exception stress or worry. Hair loss can also happen due to poor nutrition.The best approach to stalling hair loss before it is too late is to go for medical intervention if things go out of the hand. Eating a nutritionally balanced healthy diet will also ensure that your hair is getting all the nutrients it requires, for its healthy upkeep. One good tip would also be to stay away from most commercial hair styling solutions or conditioners available in the market, since they contain high levels of chemical compounds that may not be healthy for the body.
2. Is hair restoration possible?
Hair loss could be a very stressful event for many a men, especially where it affects their social and individual lives and their confidence levels plummets. Advances in health care and hair treatments has brought new developments in hair restoration whether they are hair transplants or advanced natural protocols that can help the hair regrow in many cases.Hormonal imbalance, poor diet, aging, stress & worry are some of the factors that may cause hair loss. Taking a well balanced healthy diet that is filled with vegetables and fruits is a efficient form of making sure that hair loss is efficiently engaged with and in many cases reversed. One touted form of curative intervention is Low Level Laser therapy which is usually administered to men who suffer from androgenetic areata or hair fall caused by hereditary conditions. The results may vary between different people. It should also be understood that Laser hair regrowth is possible only in situations where the scalp and hair follicles are not severely damaged.Oral medications like Finasteride (generic version of Propecia ) has been found to help in the regrowth of hair for people who are suffering from androgenetic alopecia which is a type of hair loss because of hereditary factors. Topical medications like Minoxidil (Rogaine) which has been found to stimulate hair growth.When it comes to herbal supplements for hair restoration, Saw Palmetto is an often quoted beneficial herb to take. According to several research studies Saw Palmetto has been found to block some receptor activity on those hair follicles which are stimulated in androgenetic alopecia. Temporary hair loss that might have been caused by long term stress, environmental toxicity or because of the side effects of medications can be reversed by taking steps to mitigate these factors. One can pursue alternative practices like meditation to counter stress and also engage with alternative methods to counter the side effects that might be caused by medications.


Leave a Reply